
ISIS Offering


House Joint resolution 194
S Con Res 26
13th amendment w. 20 sections April 9. 1864
UNDRIP
Congressional Record p. A3220
Congress No longer bound by the constitution but must promote Human Rights)
Article 6 Clause 1 & 2 Constitution of USA
Unilofe Article 19 – UN international law of the sea
UNITREAL UN Convention Trade Law
1666 Cestui Qui Trust
1640 Cestui Qui Trust Act
1707 Cestui Qui Trust t Act
1666 Queen Victoria and Chief of Canada
Regina v. Ja
Export Declaration U.S. Canada & Mexico
Lean on: Rothschild, Pentagon & White House
Protocols of __ Elders of Zion
Mitsnah
Interview of Rabbi Finkelstein
1917 Trading w. t he Enemy of
Lieber Code (General Orders 100-103)
Law 89-719 US Declared Bankrupt and Insolvent
United Nations Charter Article 55 & 56
UN Declaration on Human Rights
late 14c., “relief from misfortune,” see discharge (v.). Meaning “release from work or duty” is from early 15c. Meaning “act of sending out or pouring forth” is from c. 1600; sense of “that which is emitted or poured forth” is from 1727. Meaning “action of firing off a firearm or other missile weapon” is from 1590s. Electricity sense is from 1794.
early 14c., “to exempt, exonerate, release, free (from an obligation),” from Old French deschargier “to unload, discharge” (12c., Modern French décharger), from Late Latin discarricare, from dis- “do the opposite of” (see dis-) + carricare “to load a wagon or cart,” from Latin carrus “two-wheeled wagon” (see car).
Meaning “to fulfill, to perform (one’s duties, etc.)” is from c. 1400. Sense of “dismiss from office or employment” is from c. 1400. Meaning “to unload, to free from, disburden” is late 14c. Of weapons, “send forth by propulsion,” transitive, 1550s; “to fire off,” intransitive, 1580s. Of a river, “to empty itself,” c. 1600. The electrical sense is first attested 1748. Related: Discharged; discharging.
mid-14c., determinacioun, “decision, sentence in a suit at law, definite or authoritative judicial settlement,” from Old French déterminacion “determination, settlement, definition” (14c.) and directly from Medieval Latin determinationem (nominative determinatio) “conclusion, boundary,” noun of action from past-participle stem of Latin determinare “to enclose, bound, set limits to” (see determine).
Meaning “action of definitely ascertaining” is from 1670s; that of “result ascertained, a conclusion” is from 1560s. As “fixed direction toward a goal or terminal point,” from 1650s, originally in physics or anatomy; metaphoric sense “fixation of will toward a goal, state of mental resolution with regard to something” is from 1680s; general sense of “quality of being resolute, fixedness of purpose as a character trait” is by 1822.
The Trading with the Enemy Act (TWEA) of 1917 (40 Stat. 411, codified at 12 U.S.C. § 95 and 50 U.S.C. § 4301 et seq.) is a United States federal law, enacted on October 6, 1917, that gives the President the power to oversee or restrict any and all trade between the United States and its enemies in times of war but was expanded to be usable in times of peace via congressional amendment. It was amended again alongside the passage of the International Emergency Economic Powers Act (IEEPA) to be applicable only in times of war, while the IEEPA was intended to be used in times of peace.[1][2]
TWEA is sometimes confused with the IEEPA, which grants somewhat broader powers to the President, and which is invoked during states of emergency when the United States is not at war. The IEEPA was passed in an attempt to rein in perceived abuses by the US President of the TWEA by making the powers subject to the National Emergencies Act (NEA). The NEA included a legislative veto to allow Congress to terminate a national emergency with a concurrent resolution.[3] However, the U.S. Supreme Court found such legislative vetoes unconstitutional in Immigration and Naturalization Service v. Chadha. Following the Court’s decision, Congress amended the NEA to require a joint resolution.[4]
As of 2018, Cuba is the only country restricted under the Act. North Korea was removed from the provisions of the Act in 2008, although restrictions under IEEPA authority remain in effect.[5][6]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trading_with_the_Enemy_Act_of_1917
The District of Columbia Organic Act of 1871 is an Act of Congress that repealed the individual charters of the cities of Washington and Georgetown and established a new territorial government for the whole District of Columbia. Though Congress repealed the territorial government in 1874, the legislation was the first to create a single municipal government for the federal district.[1]
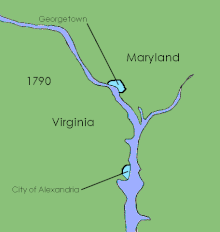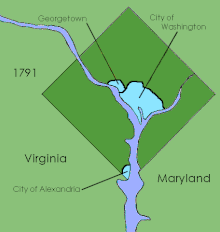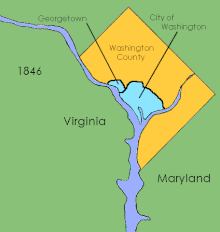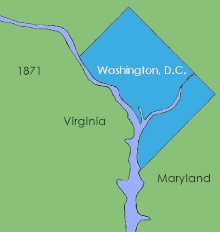
Evolution of the District’s internal boundaries
The passage of the Residence Act in 1790 created a new federal district that would become the capital of the United States. Formed from land donated by the states of Maryland and Virginia, the capital territory already included two large settlements at its creation: the port of Georgetown, Maryland and the town of Alexandria, Virginia. A new capital city named in honor of President George Washington was founded to the east of Georgetown in 1791.
Shortly after establishing operations in the new capital, Congress passed the Organic Act of 1801, which organized the federal territory. The territory within the federal district east of the Potomac formed the new County of Washington, which was governed by a levy court consisting of seven to eleven Justices of the Peace appointed by the President, and was governed by Maryland law as of 1801. The area west of the river became Alexandria County which was governed by Virginia law. In addition, Congress allowed the cities of Washington, Alexandria and Georgetown to each maintain their own municipal governments. In 1846 Alexandria County was returned by Congress to the state of Virginia.
The outbreak of the American Civil War in 1861 led to notable growth in the capital’s population due to the expansion of the federal government and a large influx of emancipated slaves.[2] By 1870, the District’s population had grown 75% to nearly 132,000 residents.[3] Growth was even more dramatic within the County of Washington, where the population more than doubled as people escaped the crowded city.[4]
The individual local governments within the District were insufficient to handle the population growth. Living conditions were poor throughout the capital, which still had dirt roads and lacked basic sanitation. The situation was so bad that some lawmakers in Congress even suggested moving the capital out further west, but President Ulysses S. Grant refused to consider the proposals.[5]
Instead, Congress passed the Organic Act of 1871, which revoked the individual charters of the cities of Washington and Georgetown and combined them with Washington County to create a unified territorial government for the entire District of Columbia.[6] The new government consisted of an appointed governor and 11-member council, a locally elected 22-member assembly, and a board of public works charged with modernizing the city.[7] The Seal of the District of Columbia features the date 1871, recognizing the year the District’s government was incorporated.[8]
The Act did not establish a new city or city government within the District. Regarding a city of Washington, it stated that “that portion of said District included within the present limits of the city of Washington shall continue to be known as the city of Washington”. In the present day, the name “Washington” is commonly used to refer to the entire District, but DC law continues to use the definition of the city of Washington as given in the Organic Act.[9]
In 1873, President Grant appointed an influential member of the board of public works, Alexander Robey Shepherd, to the post of governor. Shepherd authorized large-scale municipal projects, which greatly modernized Washington. In doing so however, the governor spent three times the money that had been budgeted for capital improvements, bankrupting the city.[10] In 1874, Congress replaced the District’s quasi-elected territorial government with an appointed three-member Board of Commissioners. Direct rule by Congress continued until the passage of the District of Columbia Home Rule Act in 1973.[11]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/District_of_Columbia_Organic_Act_of_1871
(a)Discriminatory practices prohibited; employees or applicants for employment subject to coverage
All personnel actions affecting employees or applicants for employment (except with regard to aliens employed outside the limits of the United States) in military departments as defined in section 102 of title 5, in executive agencies as defined in section 105 of title 5 (including employees and applicants for employment who are paid from nonappropriated funds), in the United States Postal Service and the Postal Regulatory Commission, in those units of the Government of the District of Columbia having positions in the competitive service, and in those units of the judicial branch of the Federal Government having positions in the competitive service, in the Smithsonian Institution, and in the Government Publishing Office, the Government Accountability Office, and the Library of Congress shall be made free from any discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin.(b)Equal Employment Opportunity Commission; enforcement powers; issuance of rules, regulations, etc.; annual review and approval of national and regional equal employment opportunity plans; review and evaluation of equal employment opportunity programs and publication of progress reports; consultations with interested parties; compliance with rules, regulations, etc.; contents of national and regional equal employment opportunity plans; authority of Librarian of CongressExcept as otherwise provided in this subsection, the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission shall have authority to enforce the provisions of subsection (a) through appropriate remedies, including reinstatement or hiring of employees with or without back pay, as will effectuate the policies of this section, and shall issue such rules, regulations, orders and instructions as it deems necessary and appropriate to carry out its responsibilities under this section. The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission shall—(1)be responsible for the annual review and approval of a national and regional equal employment opportunity plan which each department and agency and each appropriate unit referred to in subsection (a) of this section shall submit in order to maintain an affirmative program of equal employment opportunity for all such employees and applicants for employment;(2)be responsible for the review and evaluation of the operation of all agency equal employment opportunity programs, periodically obtaining and publishing (on at least a semiannual basis) progress reports from each such department, agency, or unit; and(3)consult with and solicit the recommendations of interested individuals, groups, and organizations relating to equal employment opportunity.The head of each such department, agency, or unit shall comply with such rules, regulations, orders, and instructions which shall include a provision that an employee or applicant for employment shall be notified of any final action taken on any complaint of discrimination filed by him thereunder. The plan submitted by each department, agency, and unit shall include, but not be limited to—(1)provision for the establishment of training and education programs designed to provide a maximum opportunity for employees to advance so as to perform at their highest potential; and(2)a description of the qualifications in terms of training and experience relating to equal employment opportunity for the principal and operating officials of each such department, agency, or unit responsible for carrying out the equal employment opportunity program and of the allocation of personnel and resources proposed by such department, agency, or unit to carry out its equal employment opportunity program.With respect to employment in the Library of Congress, authorities granted in this subsection to the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission shall be exercised by the Librarian of Congress.(c)Civil action by employee or applicant for employment for redress of grievances; time for bringing of action; head of department, agency, or unit as defendant
Within 90 days of receipt of notice of final action taken by a department, agency, or unit referred to in subsection (a), or by the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission upon an appeal from a decision or order of such department, agency, or unit on a complaint of discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex or national origin, brought pursuant to subsection (a) of this section, Executive Order 11478 or any succeeding Executive orders, or after one hundred and eighty days from the filing of the initial charge with the department, agency, or unit or with the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission on appeal from a decision or order of such department, agency, or unit until such time as final action may be taken by a department, agency, or unit, an employee or applicant for employment, if aggrieved by the final disposition of his complaint, or by the failure to take final action on his complaint, may file a civil action as provided in section 2000e–5 of this title, in which civil action the head of the department, agency, or unit, as appropriate, shall be the defendant.(d)Section 2000e–5(f) through (k) of this title applicable to civil actions
The provisions of section 2000e–5(f) through (k) of this title, as applicable, shall govern civil actions brought hereunder, and the same interest to compensate for delay in payment shall be available as in cases involving nonpublic parties..[1](e)Government agency or official not relieved of responsibility to assure nondiscrimination in employment or equal employment opportunity
Nothing contained in this Act shall relieve any Government agency or official of its or his primary responsibility to assure nondiscrimination in employment as required by the Constitution and statutes or of its or his responsibilities under Executive Order 11478 relating to equal employment opportunity in the Federal Government.(f)Section 2000e–5(e)(3) of this title applicable to compensation discrimination
Section 2000e–5(e)(3) of this title shall apply to complaints of discrimination in compensation under this section.
“interbreeding of races,” applied originally and especially to sexual union between black and white individuals, 1863, coined irregularly by U.S. journalist David Goodman Croly from Latin miscere “to mix” (from PIE root *meik- “to mix”) + genus “race,” from PIE root *gene- “give birth, beget,” with derivatives referring to procreation and familial and tribal groups. It first appeared in “Miscegenation: The Theory of the Blending of the Races, Applied to the American White Man and Negro,” a pretended anti-Abolitionist pamphlet Croly and others published anonymously in advance of the 1864 U.S. presidential election. The old word was amalgamation.
The design of “Miscegenation” was exceedingly ambitious, and the machinery employed was probably among the most ingenious and audacious ever put into operation to procure the indorsement of absurd theories and give the subject the widest notoriety. The object was to so make use of the prevailing ideas of the extremists of the Anti-Slavery party, as to induce them to accept doctrines which would be obnoxious to the great mass of the community, and which would, of course, be used in the political canvass which was to ensue. [P.T. Barnum, “The Humbugs of the World,” 1866; he also writes that, despite the pamphlet being an ingenious and impudent literary hoax, the word “has passed into the language and no future dictionary will be complete without it.”]